Describe How Fats Are Used During Exercise
When we begin to exercise we burn glucose and glycogen but it only takes a. Either source can predominate depending upon the duration and intensity of exercise degree of prior physical conditioning and the composition of the diet consumed in the days prior to a bout of exercise.

Exercise Intensity And Fuel Selection Carbohydrates Vs Fats Youtube
As exercise intensity increases carbohydrates form a larger part of your muscles fuel.
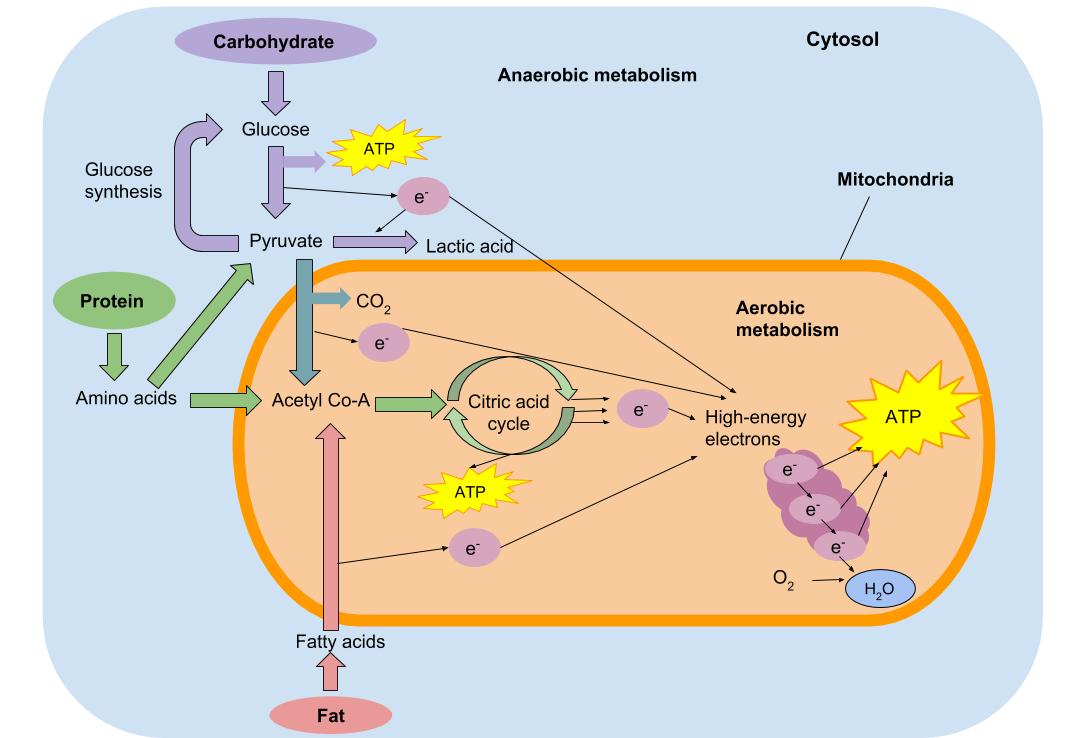
. Fats supply much more energy than carbohydrates -- 9 calories per gram versus 4 from carbs -- but fat metabolism is slow. Your body responds to this slight decrease by producing two hormones. FAT Fat is the major fuel for light-intensity to moderate-intensity exercise such as jogging hiking dance cycling and recreational swimming.
With fat reserves in the body being almost unlimited low-intensity activities are able to continue for a long time. The bodys other fuels are glucose and its storage form glycogen. This is an important distinction.
How Well-Trained You Are. The amount as well as the percentage of carbohydrate and fat used per minute are some additional parameters that are measured with the metabolic cart. If the body stores more fat then it uses the fat cells will expand causing weight gain.
Half of the energy for these activities comes from the aerobic using oxygen breakdown of muscle sugar stores glycogen and the other half comes from circulating blood sugar and fatty acids. When muscles need a steady long-lasting fuel source such. All carbs are ultimately converted to glucose and provide around 41 kcalg.
During long duration exercise the carbohydrate stored within body gets depleted within one hour. During prolonged submaximal exercise the magnitude of the con. Crossover concept from fat to CHO is due to recruitment of fast muscle fibers which increases in glycolytic enzymes Low intensity is not best for burning fat high intensity is best.
Food is made up of carbohydrates fats and proteins and these nutrients are broken down into their simplest forms glucose fatty acids and amino acids during digestion. These are anaerobic fuels meaning that they can provide energy without oxygen. Fatty acids are the primary energy source during low-intensity activity.
Depending on many factors many sports can adequately be completed with focus on nutritional preparation. If the body is forced to rely on stored fat reserves for energy whether because of diet or exercise the fat cells will shrink causing weight loss. Fatty acid oxidation can contribute 50 to 60 per cent of the energy.
When glycolysis occurs without oxygen O2 the pyruvate is converted to lactate. During low-intensity activities the body will use aerobic metabolism over anaerobic metabolism because it is more efficient by producing larger amounts of ATP. Because of this there are.
One mole of glucose yields 2 mol ATP but 1 mol glycogen yields 3 mol ATP. During short heavy exercise it may be the only energy source for the working muscle and may be derived exclusively from the glycogen stores within the muscle fibers themselves. This is where it gets a little sticky and confusing for the average person.
Are Carbohydrates Fats or Proteins Used During Cardiovascular Exercise. During low-intensity exercise fat is the primary source of fuel your body uses. If you regularly do aerobic exercise and have developed a certain level of aerobic fitness your body.
Breathing during activity they are able to use more fat for production of energy. Fat and carbohydrate are the two major energy sources used during exercise. Role of carbohydrate in exercise.
Therefore the long duration whether moderate intensity activity may result in more use of body fat stores. During exercise and physical activity the primary fuels used by muscles are carbohydrate and fat. Protein also provides 41 kcalg and is broken down into amino acids.
During low-intensity cardiovascular exercise fats are your muscles primary fuel. Exercise can cause a slight drop in blood sugar the amount of glucose circulating in your bloodstream. Our carbohydrate and fat storage covers most fuel needs if well.
The process of glycolysis through which glucose or glycogen is broken down to pyruvate. More efficient during exercise to use glycogen then circulating glucose. Therefore while it is true that fat contributes a greater percentage of the total energy during lower intensity exercise at higher intensity exercise the total quantity of fat utilized may be greater for exercise performed for an equivalent period of time.
When you work out your muscles use energy which they derive by metabolizing fats and carbohydrates. Fats are less readily available for energy but they provide 91 kcalg after being converted into free fatty acids. At higher exercise intensities total fat oxidation is higher because TEE is higher.
Carbohydrate fuel comes in the form of muscle glycogen and blood glucose. Able to burn more calories which means burning more fat. The 3 main sources of fuel during exercise are carbohydrates fats and proteins.
The amount and the percentage of carbohydratefat used by the body are two entirely different things. The liver and muscles react to the hormonal changes by converting the stored glycogen into glucose and releasing this substance into the blood stream for immediate. When mild exercise is performed there is a tendency to burn relatively more fat and less glucose.
As exercise intensity increases the number of calories burned also increases. As a result the fat present in body started acting as the main source of energy. Fat Oxidation During Exercise.
Our muscles are primed to burn fat and it is our most concentrated form of energy. Carbohydrate is an important energy source during exercise. Once these nutrients are broken down they are transported through the blood to either be used in a metabolic pathway or stored for later use.
Keep in mind that your body uses a combination of fat carbohydrates and protein at all times but the percentage changes depending upon exercise intensity and duration. They provide a slow-burning. However fat cells can increase and decrease in size depending on the amount of fat that the body is storing.
And the increased stability of fat to be oxidized within the skeletal muscle is thought to contribute in part to why regular exercise helps in reducing body mass in particular body fat levels because of this greater ability to oxidize fat in skeletal muscle rather than to store that fat in adipose tissue. During moderate to high intensity exercise the body uses predominantly carbohydrate as a fuel source as well as some fat storage.

Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
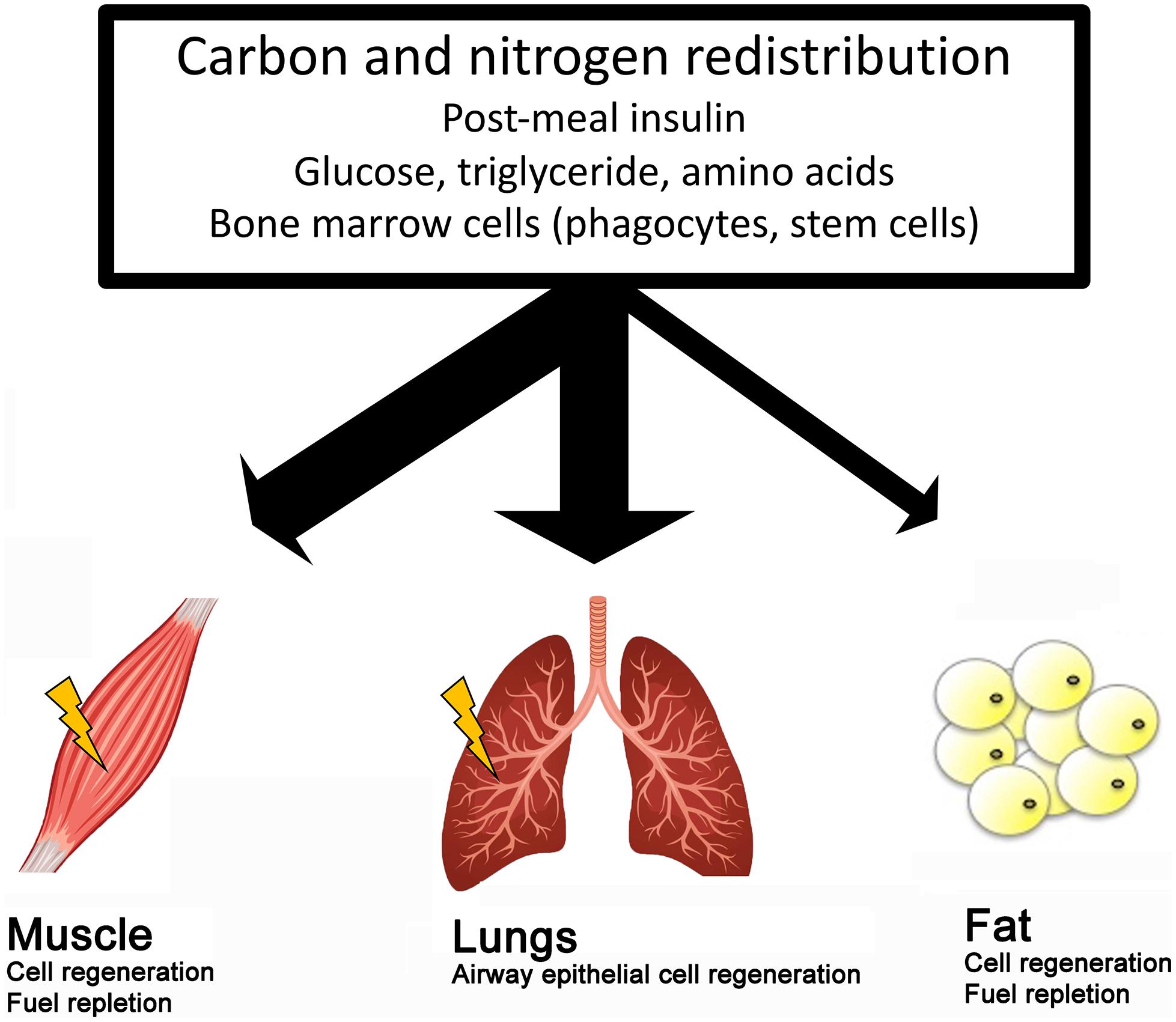
Frontiers Scientific Challenges On Theory Of Fat Burning By Exercise Physiology
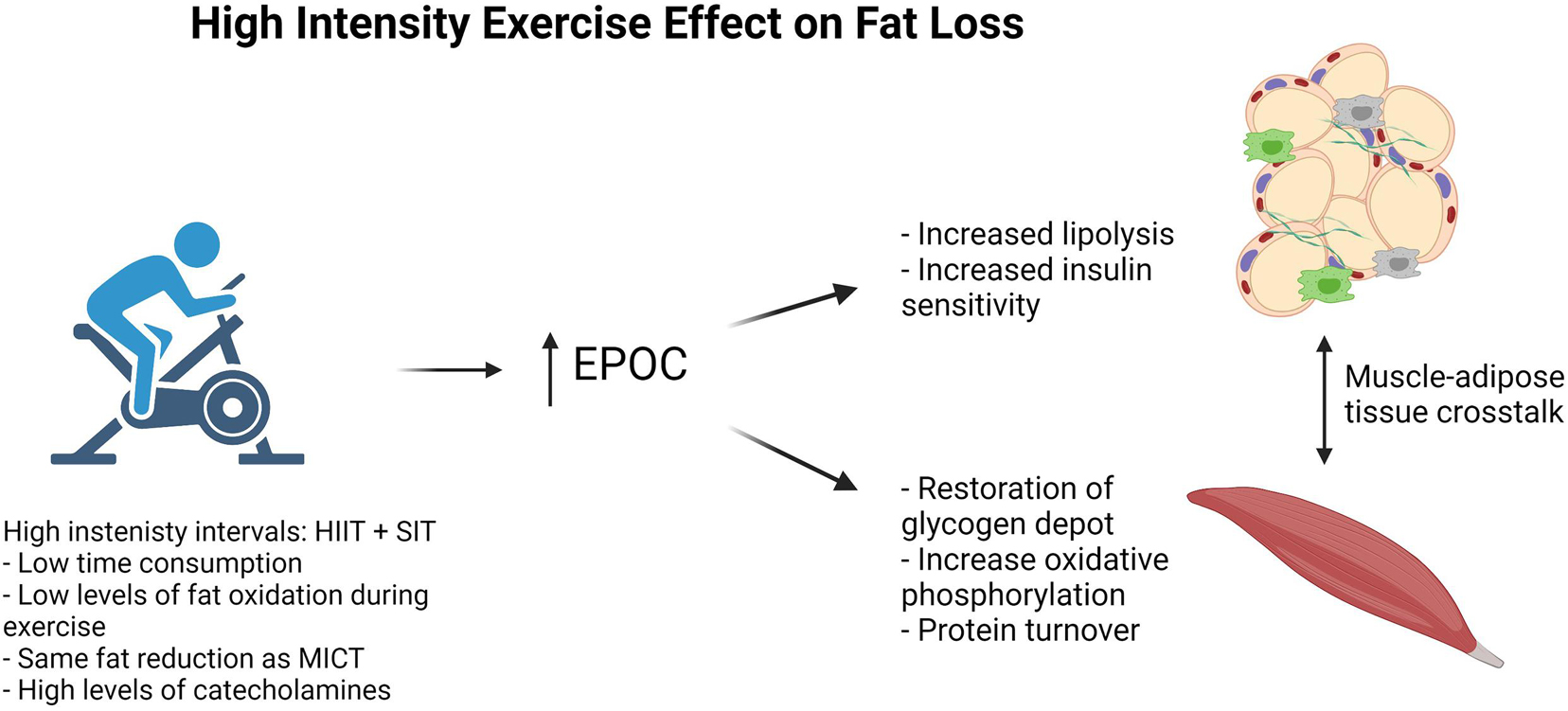
Frontiers Effect Of Exercise Training On Fat Loss Energetic Perspectives And The Role Of Improved Adipose Tissue Function And Body Fat Distribution Physiology
No comments for "Describe How Fats Are Used During Exercise"
Post a Comment